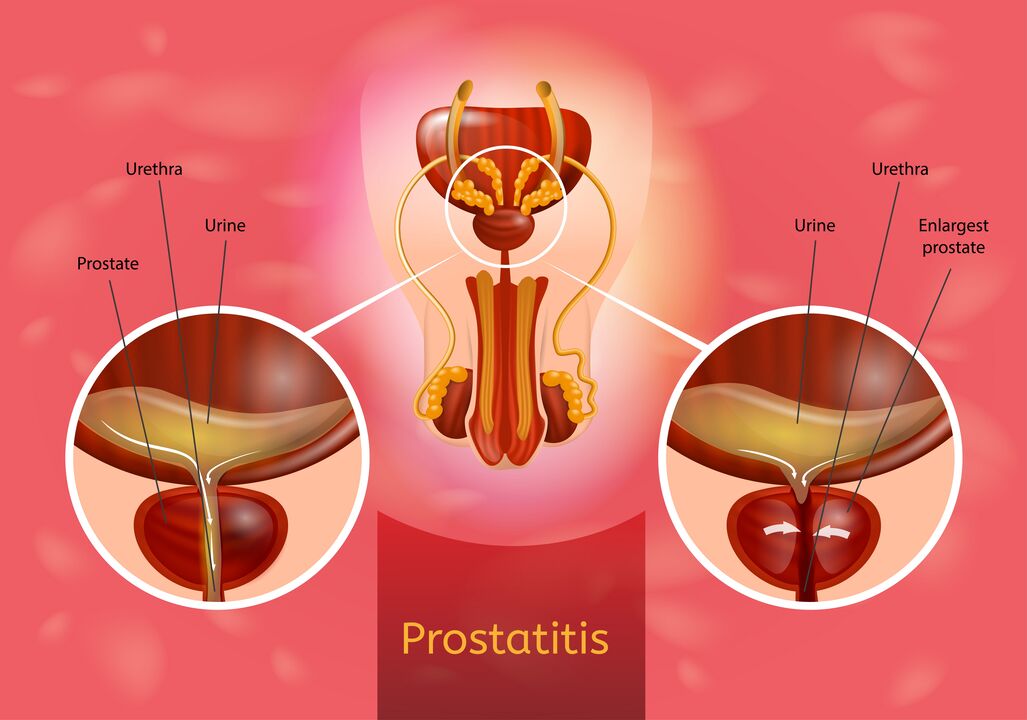
Prostatitis is the disease of prostate glands (prostate), which is developing as a result of inflammatory changes in it.According to statistics, the prevalence of the disease reaches 35-50% and is revealed in men aged 20-40 years.
Types
4 forms of prostatitis differ:
- acute (bacterial);
- Chronic bacterial;
- Chronic non-decacterial;
- Asymptomatic chronic.
Acute prostatitis is very rare due to the rapid flow of the inflammatory process and the immediate transition into the chronic phase (false improvement).
Chronic untouched prostatitis, otherwise, is called chronic syndrome in poultry pain, may have inflammatory (with the presence of urine and the ejaculation of high leukocytes), not inflammatory in nature.
Reasons
The cause of acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis are pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi).The most common is the source of inflammation:
- E. coli;
- Streptococks;
- Staphylococci;
- Proteus;
- Klebsiella;
- Pseudomonic stick;
- Pathogens sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, mycoplasma, gonoscoli, trichomone, cytomegalovirus and others).
Most microorganisms are in the intestines, on the skin, but entering the prostate tissue, cause the inflammatory process.As a rule, the cause of the disease is not a pathogen, but a team of several types of microbes.
The development of chronic prostatitis can cause the following factors:
- Concomitant diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis);
- Sedentary lifestyle ("sedentary" work);
- inclination to prison;
- weakening body defense;
- injuries;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Alcohol abuse and smoking;
- Random sexual intercourse;
- Irregular sex life (long abstinence);
- interrupted a sexual intercourse;
- Irregular bladder discharge;
- dissatisfied sexual desire;
- Chronic progress;
- hypothermia;
- The presence of carious teeth and other sources of chronic infection (for example, chronic tonsilitis).
Prostatitis symptoms
Acute prostatitis is a very insidious disease.It is quite difficult to "catch", because first, the process becomes chronic very quickly, and the other, most patients prefer a "sink" manifestation of the house.Prostate inflammation patients often refer to the doctor in advanced cases with erection disorders and other consequences.
The acute form of the disease is done against the background:
- fever;
- Chills;
- Other descriptions (weakness, lethargy, loss of appetite, etc.).
Inflammation of prostate accompanied by pain in the perineum, in an inguinal region and in the scrotum.
It is also characteristic of painful and fast urination.Sometimes u urine can notice whitish gesture discharge.
In addition, the patient may pay attention to the lack of nights and morning erection, the poor erection of the bad team during the intimacy and sharply shortening of sexual intercourse.
Typical symptoms of urination disorders occur: weak stream and frequent instincts, although urine stands out a little.
In the future, in the absence of treatment, chronic prostatitis reaches APOGEI: the procedures of sexual function appear.For example:
- insufficient erection or his absence;
- Painful erections, which is why the patient avoids sexual intercourse;
- Deleted orgasm;
- a brief relationship;
- Ejaculation ability.
The chronic acacterial prostatitis is 95% among all prostatitis, mostly suffer from men for about 30 years.It is characterized by permanent or periodic pagos in the pelvis, prostate, in the scrotum, while in laboratory analyzes there are no signs of inflammation.The causes of the disease are definitely not established.
Diagnostics
In the diagnosis of acute and chronic prostatitis, in addition to collecting complaints, anamnesis and patient studies, the following methods are used:
- General blood and urine test;
- Microscopic overview of the secret prostate and sowing is on nutrient media detection media (the secret is obtained after the finger massage prostate in the rectum);
- Cytological study of urine;
- Ultrasound of prostate and pelvic authorities;
- Calculated tomography and nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Development from the urethra on the microflor.
Differential diagnosis aims to distinguish prostatitis, prostate adenoma, prostate cancer, stones in prostate.
Complete list of diagnostic procedures and drug treatment for prostatitis in the 2012 Assistant Standard.
Prostatitis treatment
The same symptoms can be signs of various diseases, and the disease cannot occur in accordance with the textbook.Don't try to consult your doctor toward you.The surgeon-urologist leads to prostatitis.
The purpose of ethithropic treatment focused on eliminating the causes of prostatitis is the removal of pathogens.Depending on the identified cause, antibiotics, antivirus or antifungal medications are prescribed.The duration of acute prostatitis therapy is 7-10 days, in a chronic process - 4-8 weeks.
To treat bacterial infection are used:
- antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin);
- macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin);
- Doxycycline;
- Antibacterial medications.
Antifungal (Diflucan, Fluconazole) is prescribed orally in rectal candles.
In addition, other types of therapy are used:
- Anti -allergic (Suprastin, Claritin, Dimendrol);
- Anti -infalmatory (indometacin, diclofenak);
- Anesthetic (without bar, analgin, boralgin).
Also appointed:
- Physiotherapy;
- Medical gymnastics;
- Prostate massage.
The whole course of treatment lasts 3-4 months.
Prevention
The following conditions must be observed for the prevention of the disease:
- Regular sex life;
- Discard bad habits;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle (playing sports, walking in fresh air);
- compliance with a diet;
- Regular visits to urologist.